笔记:
基础数据类型:
SEL:
SEL又叫选择器,是表示一个方法的selector的指针
Objective-C在编译时,会依据每一个方法的名字、参数序列,生成一个唯一的整型标识(Int类型的地址),这个标识就是SEL
1 | SEL sel1 = @selector(method1); |
1 | 输出:RuntimeTest[52734:466626] sel : 0x100002d72 |
注意点:
在 Objective-C同一个类(及类的继承体系)中,不能存在2个同名的方法
不同类的实例对象执行相同的selector时,会在各自的方法列表中去根据selector去寻找自己对应的IMP
工程中的所有的SEL组成一个Set集合,Set的特点就是唯一,因此SEL是唯一的。因此,如果我们想到这个方法集合中查找某个方法时,只需要去 找到这个方法对应的SEL就行了,SEL实际上就是根据方法名hash化了的一个字符串,而对于字符串的比较仅仅需要比较他们的地址就可以,效率高
IMP
IMP实际上是一个函数指针,指向方法实现的首地址
定义如下:
1 | id (*IMP)(id, SEL, …) |
这个函数使用当前CPU架构实现的标准的C调用约定。第一个参数是指向self的指针(如果是实例方法,则是类实例的内存地址;如果是类方法,则是指向元类的指针),第二个参数是方法选择器(selector),接下来是方法的实际参数列表。
由于每个方法对应唯一的SEL,因此我们可以通过SEL方便快速准确地获得它所对应的 IMP,查找过程将在下面讨论。取得IMP后,我们就获得了执行这个方法代码的入口点,此时,我们就可以像调用普通的C语言函数一样来使用这个函数指针了
Method
1 | typedef struct objc_method *Method; |
该结构体中包含一个SEL和IMP,实际上相当于在SEL和IMP之间作了一个映射。有了SEL,我们便可以找到对应的IMP,从而调用方法的实现代码
方法相关操作函数
1 | // 调用指定方法的实现 |
方法调用流程
在Objective-C中,消息直到运行时才绑定到方法实现上。编译器会将消息表达式[receiver message]转化为一个消息函数的调用,即objc_msgSend。
1 | objc_msgSend(receiver, selector) |
当消息发送给一个对象时,objc_msgSend通过对象的isa指针获取到类的结构体,然后在方法分发表里面查找方法的selector。如果 没有找到selector,则通过objc_msgSend结构体中的指向父类的指针找到其父类,并在父类的分发表里面查找方法的selector。依 此,会一直沿着类的继承体系到达NSObject类。一旦定位到selector,函数会就获取到了实现的入口点,并传入相应的参数来执行方法的具体实 现。如果最后没有定位到selector,则会走消息转发流程。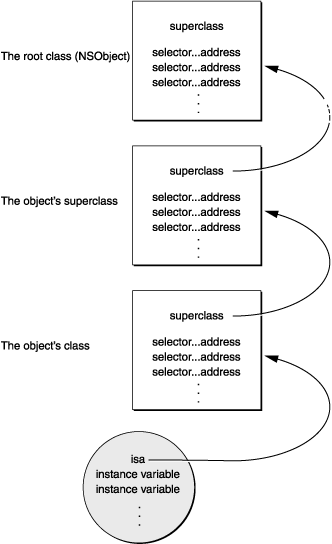
隐藏参数
objc_msgSend有两个隐藏参数:
- 消息接收对象
- 方法的selector
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9- strange
{
id target = getTheReceiver();
SEL method = getTheMethod();
if ( target == self || method == _cmd )
return nil;
return [target performSelector:method];
}
获取方法地址
NSObject类提供了methodForSelector:方法,让我们可以获取到方法的指针,然后通过这个指针来调用实现代码。我们需要将methodForSelector:返回的指针转换为合适的函数类型,函数参数和返回值都需要匹配上。
1 | void (*setter)(id, SEL, BOOL); |
消息转发
当一个对象无法接收某一消息时,就会启动所谓”消息转发(message forwarding)“机制,通过这一机制,我们可以告诉对象如何处理未知的消息。默认情况下,对象接收到未知的消息,会导致程序崩溃,控制台输出异常信息。
消息转发机制基本上分为三个步骤:
动态方法解析
对象在接收到未知的消息时,首先会调用所属类的类方法+resolveInstanceMethod:(实例方法)或 者+resolveClassMethod:(类方法)。在这个方法中,我们有机会为该未知消息新增一个”处理方法”“。不过使用该方法的前提是我们已经 实现了该”处理方法”,只需要在运行时通过class_addMethod函数动态添加到类里面就可以了。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14void functionForMethod1(id self, SEL _cmd) {
NSLog(@"%@, %p", self, _cmd);
}
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel {
NSString *selectorString = NSStringFromSelector(sel);
if ([selectorString isEqualToString:@"method1"]) {
class_addMethod(self.class, @selector(method1), (IMP)functionForMethod1, "@:");
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}备用接收者
如果一个对象实现了这个方法,并返回一个非nil的结果,则这个对象会作为消息的新接收者,且消息会被分发到这个对象。当然这个对象不能是self自身,否则就是出现无限循环。当然,如果我们没有指定相应的对象来处理aSelector,则应该调用父类的实现来返回结果。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56@interface SUTRuntimeMethodHelper : NSObject
- (void)method2;
@end
@implementation SUTRuntimeMethodHelper
- (void)method2 {
NSLog(@"%@, %p", self, _cmd);
}
@end
#pragma mark -
@interface SUTRuntimeMethod () {
SUTRuntimeMethodHelper *_helper;
}
@end
@implementation SUTRuntimeMethod
+ (instancetype)object {
return [[self alloc] init];
}
- (instancetype)init {
self = [super init];
if (self != nil) {
_helper = [[SUTRuntimeMethodHelper alloc] init];
}
return self;
}
- (void)test {
[self performSelector:@selector(method2)];
}
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
NSLog(@"forwardingTargetForSelector");
NSString *selectorString = NSStringFromSelector(aSelector);
// 将消息转发给_helper来处理
if ([selectorString isEqualToString:@"method2"]) {
return _helper;
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
@end完整转发
运行时系统会在这一步给消息接收者最后一次机会将消息转发给其它对象。对象会创建一个表示消息的NSInvocation对象,把与尚未处理的消息 有关的全部细节都封装在anInvocation中,包括selector,目标(target)和参数。我们可以在forwardInvocation 方法中选择将消息转发给其它对象。
forwardInvocation:方法的实现有两个任务:
- 定位可以响应封装在anInvocation中的消息的对象。这个对象不需要能处理所有未知消息。
- 使用anInvocation作为参数,将消息发送到选中的对象。anInvocation将会保留调用结果,运行时系统会提取这一结果并将其发送到消息的原始发送者。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
NSMethodSignature *signature = [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
if (!signature) {
if ([SUTRuntimeMethodHelper instancesRespondToSelector:aSelector]) {
signature = [SUTRuntimeMethodHelper instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
}
return signature;
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation {
if ([SUTRuntimeMethodHelper instancesRespondToSelector:anInvocation.selector]) {
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:_helper];
}
}